

Select the suitable control chart for your processes.If not, the chart is likely to give more false forecasts for the tests, indicating that your processes are out of control when they are not.”- Pankaj Tyagi, Quality Control Specialist.
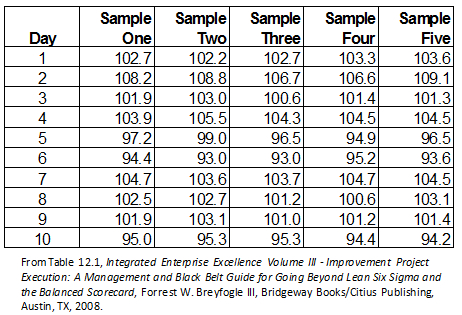
“If you are thinking of using the Individual Charts more often, you should first ascertain if the individual sample results are normally distributed. If the data elements are exceeding the control limits, the operator would immediately adjust.īenefit#5: The chart can be used to identify statistically unnatural patterns and decide when to take action. Moreover, since the processes are in statistical control, you can predict how the processes will perform in the future.īenefit#4: The objective of plotting the control chart is to identify any variation in the process. If your processes are in statistical control (indicating the consistency in individual sample results or successive sample results over time), the average on the Individuals chart is your population average that can be used to calculate the population standard deviation. can be corrected and normal output can be resumed.īenefit#3: While it is not possible to subgroup data elements due to low frequency, you can use the control chart for the assessment of results. Common variations arising due to material, machines, time, etc. This allows you to establish whether or not your process is in statistical control for each sample collected.īenefit#2: Control charts (X-Bar and R Charts) are useful in a manufacturing or production environment to control, examine, and improve a process. You can plot an element on the chart for each sample collected. 5 Benefits of Using Individuals Control Chartīenefit#1: Individuals’ control charts can be used when you have a single data element to represent a given situation. The chart monitors variation in sample results over time and checks whether the process is in control.”-Sanket Saha, Process Manager. “Usually, the X-Bar Chart is combined with an R-Chart to inspect processes where data is not available frequently. The chart indicates short-term variation or how the range of subgroup varies over time. The chart indicates long-term variation in the process or how the mean or average changes over time.Ĭhart2: Represents Moving Range (R) between consecutive individual samples. Like other variables control charts, it contains two charts:Ĭhart1: Represents Individual Sample Result (X). The chart is useful when you have just one data point at a given time to depict a situation. The Individuals control chart helps in examining variation in the data elements. Find our Upcoming Batches of Six Sigma Green Belt Certificate :- Batch


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
